第 1 集 FIFO 先来先淘汰算法分析和编码实战
简介: FIFO 先来先淘汰算法分析和编码实战
-
背景
-
在设计一个系统的时候,由于数据库的读取速度远小于内存的读取速度
-
为加快读取速度,将一部分数据放到内存中称为缓存,但内存容量是有限的,当要缓存的数据超出容量,就需要删除部分数据
-
这时候需要设计一种淘汰机制,看哪些数据删除,哪些数据保留
-
常见的有 FIFO、LRU、LFU 等淘汰算法
-
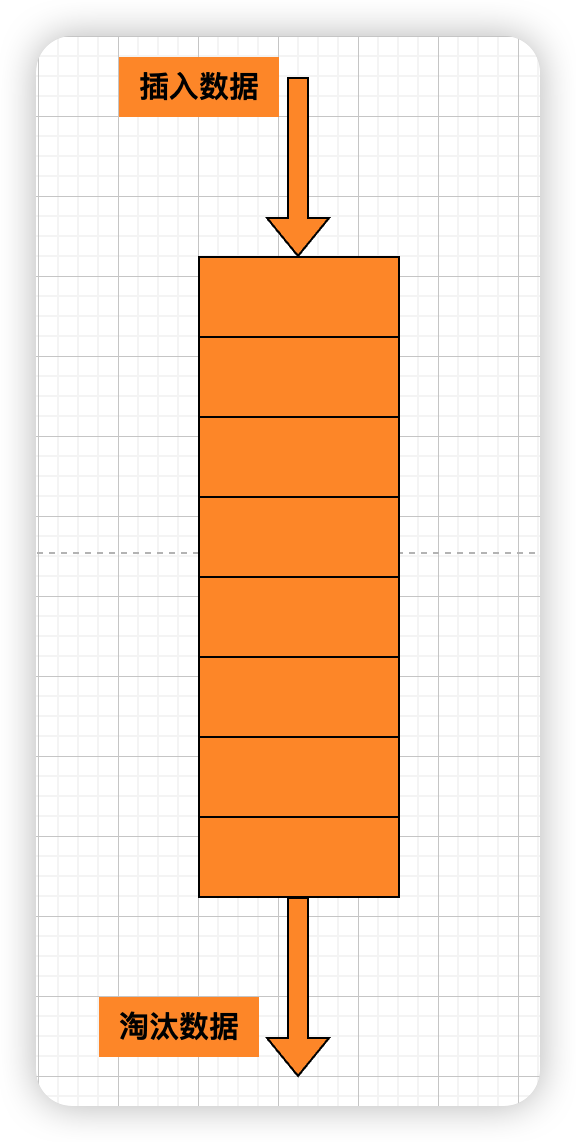
什么是 FIFO 淘汰算法
- First In First Out,先进先出,淘汰最早被缓存的对象
- 是一种常用的缓存淘汰算法,它的原理是按照先进先出的原则
- 当缓存满了之后,先将最早进入缓存的数据淘汰掉,以腾出空间给新的数据
- 优点
- 在于实现简单,不需要记录或统计数据的使用次数,只需要记录每个数据进入缓存的时间和每个数据在缓存中的位置即可
- 缺点
- 在于它不能有效地淘汰最近最少使用的数据
- 最近最少使用的数据可能会被淘汰掉,而最近最多使用的数据也可能被淘汰掉,这样就会导致缓存的效率不够高。
-
编码实现
public class FIFOCache<K, V> {
// 定义缓存的最大容量
private int maxSize;
// 定义当前缓存的容量
private int curSize;
// 用于存放缓存的key
private LinkedList<K> cacheKey;
// 用于存放缓存的value
private HashMap<K, V> cacheValue;
// 读写锁,保证线程安全
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 构造函数
public FIFOCache(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.curSize = 0;
this.cacheKey = new LinkedList<K>();
this.cacheValue = new HashMap<K, V>();
}
// 向缓存插入key-value
public void put(K key, V value) {
// 加锁保证线程安全
lock.lock();
try {
// 如果缓存已满,则删除最老的key
if (curSize == maxSize) {
K oldKey = cacheKey.removeFirst();
cacheValue.remove(oldKey);
curSize--;
}
// 插入key-value
cacheKey.addLast(key);
cacheValue.put(key, value);
curSize++;
} finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 查询指定key的value
public V get(K key) {
return cacheValue.get(key);
}
public void printKeys() {
System.out.println(this.cacheKey.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FIFOCache cache = new FIFOCache<String, String>(5);
cache.put("A", "学习springboot,在小滴课堂");
cache.put("B", "架构大课是最强面试大课");
cache.put("C", "Redis分布式缓存最主流");
cache.put("D", "海量数据项目大课是营销短链平台项目");
cache.put("E", "ElasticSearch是搜索框架");
cache.printKeys();
cache.put("F", "Flink实时计算");
cache.printKeys();
Object cacheObj1 = cache.get("G");
System.out.println("cacheObj1=" + cacheObj1);
Object cacheObj2 = cache.get("C");
System.out.println("cacheObj2=" + cacheObj2);
}
}
第 2 集 LRU 最久未使用算法原理分析和编码实战
简介: LRU 最久未使用算法原理分析和编码实战
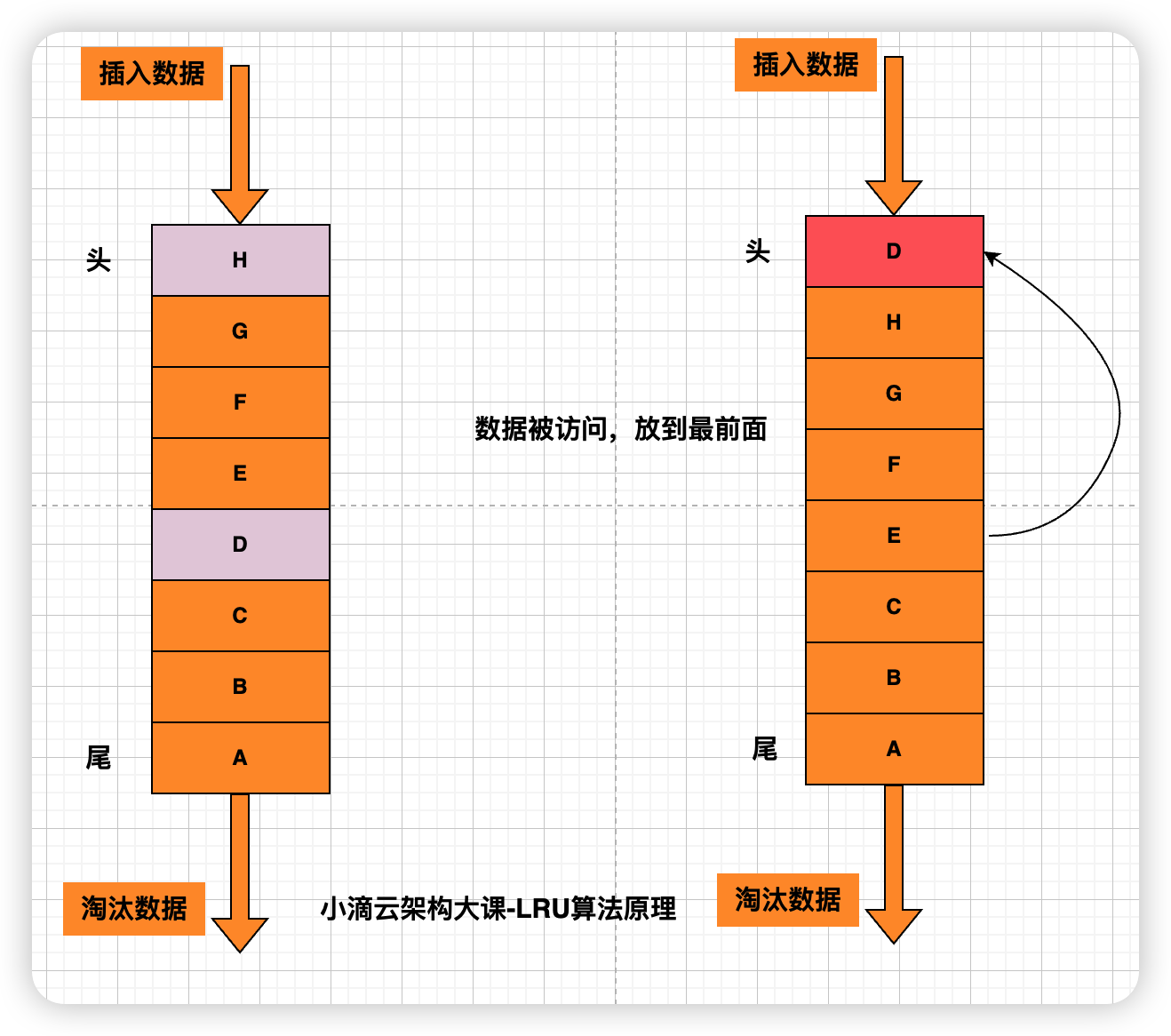
- 什么是 LRU 算法
- Least Recently Used 淘汰算法以时间作为参考,淘汰最长时间未被使用的数据
- 如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高;会淘汰最长时间没有被使用的元素(都没人要你了,不淘汰你淘汰谁)
- 基本原理是:在缓存满时,将最近最久未使用的数据淘汰出缓存,以便给新的数据留出空间。
- 实现方式可以用:数组、链表等方式
- 新插入的数据放在头部,最近访问过的也移到头部,空间满时将尾部元素删除
-
编码实现
public class LRUCache {
//用于存储key-value数据
private HashMap<String, String> map;
//用于存储key的顺序
private ArrayList<String> list;
//数组的容量
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 查询key对应的value
* @param key 键
* @return value 值
*/
public String get(String key) {
//如果key存在,则将key移动到最前端
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
list.remove(key);
list.add(0, key);
return map.get(key);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 向缓存中插入key-value
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
public void put(String key, String value) {
//如果key存在,则将key移动到最前端
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
list.remove(key);
list.add(0, key);
map.put(key, value);
} else {
//如果key不存在,则添加key-value
if (list.size() >= capacity) {
//如果容量已满,则删除最后一个key
String lastKey = list.get(list.size() - 1);
list.remove(lastKey);
map.remove(lastKey);
}
list.add(0, key);
map.put(key, value);
}
}
public void showList(){
System.out.println(list.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(5);
cache.put("A", "学习springboot,在小滴课堂");
cache.put("B", "架构大课是最强面试大课");
cache.put("C", "Redis分布式缓存最主流");
cache.put("D", "海量数据项目大课是营销短链平台项目");
cache.put("E", "ElasticSearch是搜索框架");
cache.showList();
Object cacheObj2 = cache.get("C");
System.out.println("cacheObj2=" + cacheObj2);
//C被访问,被放置头部
cache.showList();
cache.put("F", "Flink实时计算");
//新增了F,超过大小,A由于在尾部,被删除,F被放置头部
cache.showList();
//G节点不存在,所以不影响顺序
Object cacheObj1 = cache.get("G");
System.out.println("cacheObj1=" + cacheObj1);
cache.showList();
}
}
第 3 集 LFU 最近最少使用算法原理分析和编码实战《上》
简介: LFU 最近最少使用算法原理分析和编码实战
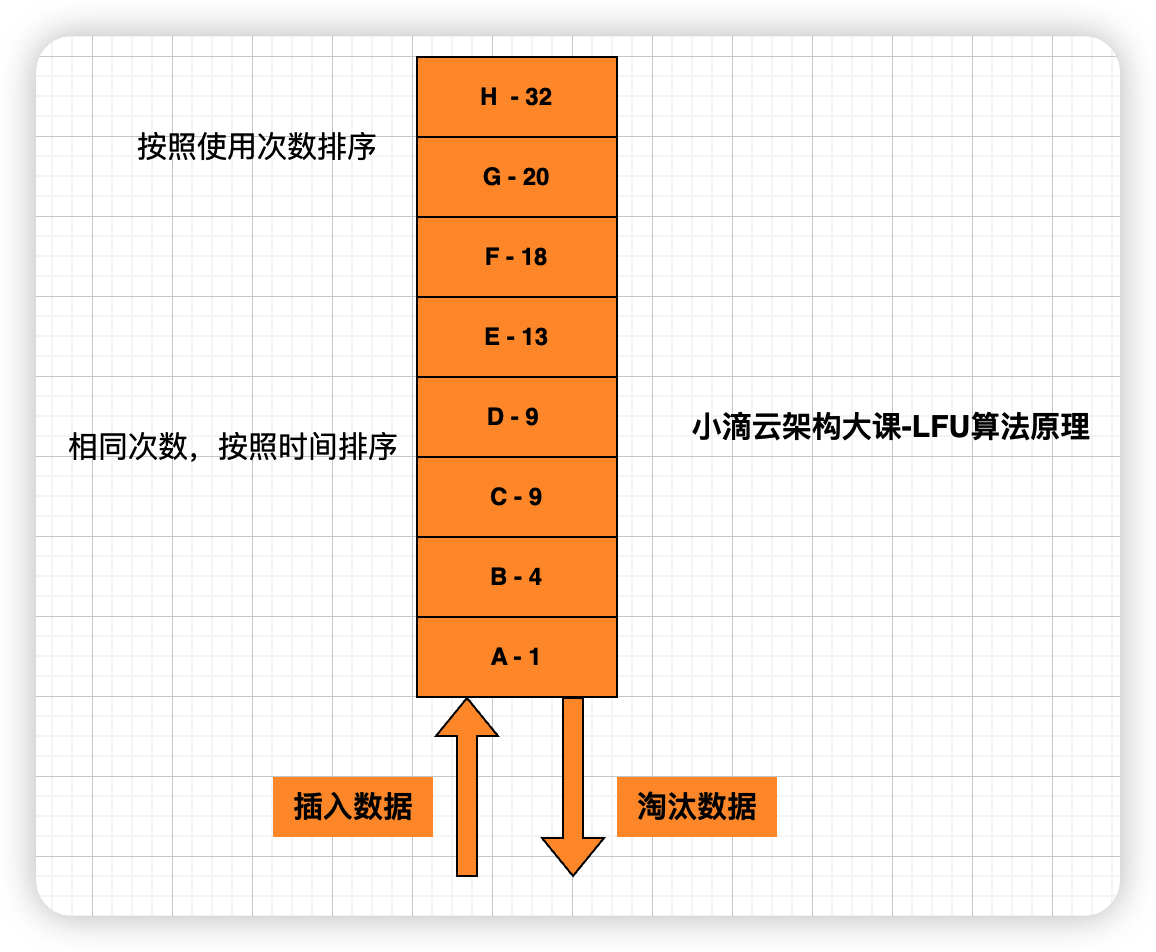
- 什么是 LFU
- Least Frequently Used 最近最少使用,表示以次数为参考,淘汰一定时期内被访问次数最少的数据
- 如果数据过去被访问多次,那么将来被访问的频率也更高
- 比 LRU 多了一个频次统计,需要时间和次数两个维度进行判断是否淘汰
- 关键流程
- 新加入数据插入到队列尾部,需要吧引用计数初始值为 1
- 当队列中的数据被访问后,对应的元素引用计数 +1,队列按【次数】重新排序,如果相同次数则按照时间排序
- 当需要淘汰数据时,将排序的队列末尾的数据删除,即访问次数最少
public class LFUCache {
//定义缓存容量
private int capacity ;
//存储key value
private Map<String,String> cache ;
//存储key的使用频次
private Map<String, CacheObj> count;
public LFUCache(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
cache = new HashMap<>();
count = new HashMap<>();
}
//存储
public void put(String key, String value) {
}
//读取
public String get(String key) {
}
//删除元素
private void removeElement() {
}
//更新相关统计频次和时间
private void addCount(String key) {
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println(cache.toString());
System.out.println(count.toString());
}
class CacheObj implements Comparable<CacheObj>{
private String key;
private int count;
private long lastTime;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public long getLastTime() {
return lastTime;
}
public void setLastTime(long lastTime) {
this.lastTime = lastTime;
}
public CacheObj(String key, int count, long lastTime) {
this.key = key;
this.count = count;
this.lastTime = lastTime;
}
//用于比较大小,如果使用次数一样,则比较时间大小
@Override
public int compareTo(CacheObj o) {
int value = Integer.compare(this.count, o.count);
return value == 0 ? Long.compare(this.lastTime, o.lastTime) : value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CacheObj{" +
"key=" + key +
", count=" + count +
", lastTime=" + lastTime +
'}';
}
}
}
第 4 集 LFU 最近最少使用算法原理分析和编码实战《下》
简介: LFU 最近最少使用算法原理分析和编码实战
public class LFUCache {
//定义缓存容量
private int capacity ;
//存储key value
private Map<String,String> cache ;
//存储key的使用频次
private Map<String, CacheObj> count;
public LFUCache(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
cache = new HashMap<>();
count = new HashMap<>();
}
//存储
public void put(String key, String value) {
String cacheValue = cache.get(key);
if (cacheValue == null) {
//新元素插入,需要判断是否超过缓存容量大小
if (cache.size() == capacity) {
removeElement();
}
count.put(key, new CacheObj(key, 1, System.currentTimeMillis()));
} else {
addCount(key);
}
cache.put(key, value);
}
//读取
public String get(String key) {
String value = cache.get(key);
if (value != null) {
addCount(key);
return value;
}
return null;
}
//删除元素
private void removeElement() {
CacheObj cacheObj = Collections.min(count.values());
cache.remove(cacheObj.getKey());
count.remove(cacheObj.getKey());
}
//更新相关统计频次和时间
private void addCount(String key) {
CacheObj cacheObj = count.get(key);
cacheObj.setCount(cacheObj.getCount()+1);
cacheObj.setLastTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println(cache.toString());
System.out.println(count.toString());
}
class CacheObj implements Comparable<CacheObj>{
private String key;
private int count;
private long lastTime;
public CacheObj(String key, int count, long lastTime) {
this.key = key;
this.count = count;
this.lastTime = lastTime;
}
//用于比较大小,如果使用次数一样,则比较时间大小
@Override
public int compareTo(CacheObj o) {
int value = Integer.compare(this.count, o.count);
return value == 0 ? Long.compare(this.lastTime, o.lastTime) : value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CacheObj{" +
"key=" + key +
", count=" + count +
", lastTime=" + lastTime +
'}';
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LFUCache cache = new LFUCache(2);
cache.put("a","aa1");
cache.put("a","aa2");
cache.showInfo();
System.out.println("---------");
String cacheValue = cache.get("a");
System.out.println(cacheValue);
cache.showInfo();
System.out.println("---------");
cache.put("b","bb1");
cache.put("b","bb2");
cache.showInfo();
System.out.println("---------");
//插入新元素,由于a的count是3,b的count是2,所以淘汰了b
cache.put("c","cc1");
cache.showInfo();
}



